Planning of Airport Ground Services
WhitepaperPlanning of ground services using the Ab Ovo Collaborative Ground Services Industry Solution
The Challenge
Every day, ground services at an airport provide services for the airlines. These are mission critical services with specific turnaround times tied to planned arrivals and departures. Living up to agreed quality and performance levels is a daily challenge, both in terms of economics and in terms of planning.
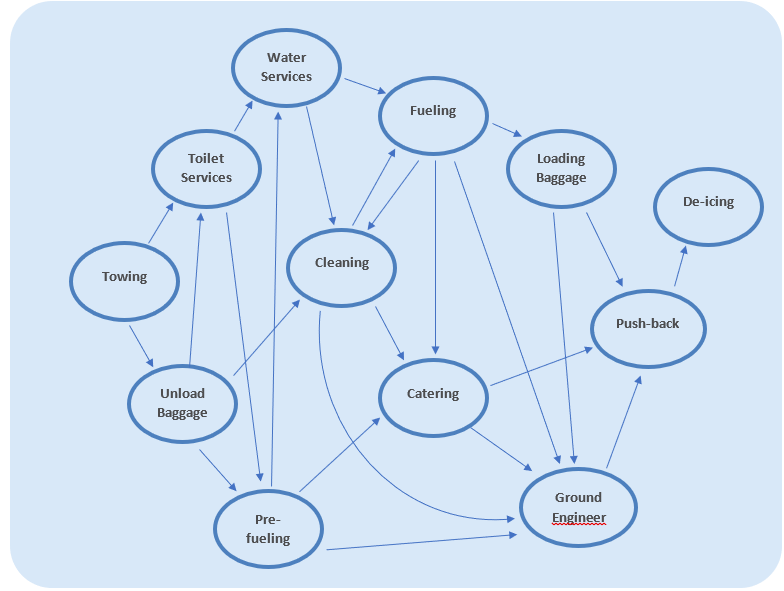
Timely performance is measured in terms of minimizing turnaround time and the delay of aircrafts, which involves a collection of dependent services that must be executed in a specific order. For example, an aircraft’s push-back from the gate can only be started when all other services are completed. An important limitation to note is that aircrafts cannot be fueled and catered at the same time.
An example of how ground services can be interdependent is shown in the figure on the right.
Planning approach
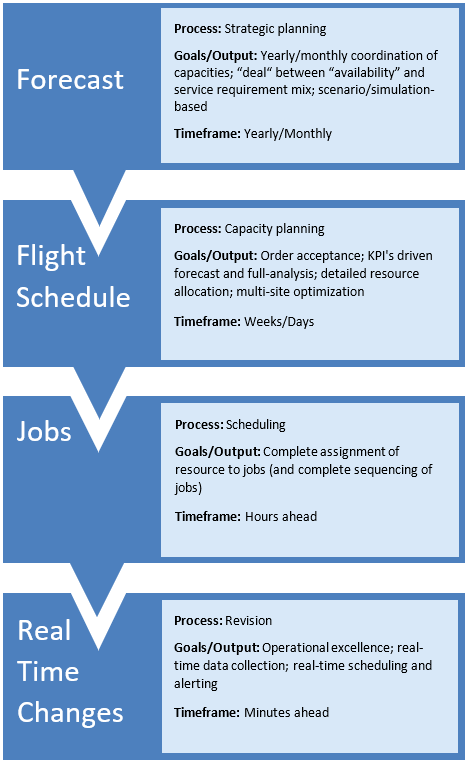
The Ab Ovo vision distinguishes four levels in the planning philosophy.
- Strategic planning
Strategic decisions (e.g., growth, consolidation, etc.) are translated into activities to obtain strategic goals, including number of resources. This supports long-term planning, which comprises a period of six-months to two years, depending on the resource types. - Capacity planning
Capacity planning comprises short-term planning of resources (e.g., holiday planning, supply of goods, etc.). The time scope is approximately a week to several months. - Scheduling
The assignment of resources to jobs is an activity that is performed up to a few hours before the actual service time. This involves all constraints to generate an optimal plan and is based on flight information. - Revision
Disturbances will influence the plan – and revisions needs to be made constantly to match again the needs. The revision planning is quick and is based on decision support for the planner to be able to make decision fast and optimal.
Load Optimization
Loading and unloading cars from trailers is a critical, time-consuming process with various constraints and regulations. Car transportation faces limits on loading weight and height, varying by location. Diverse car and trailer types, along with loading position constraints, complicate FTL and LTL shipment dispatch planning. Meeting quality and performance standards in this daily economic and planning challenge is essential.
The Ab Ovo Planning Solution
Ab Ovo has an overall, integrated vision for joint planning and scheduling of multiple ground services processes: the Ab Ovo Collaborative Ground Services Industry Solution (i.e., “C-GSIS”). This could be one integrated solution, or each of the ground services (e.g., catering, fueling, etc.), often operated by different companies, could work in a stand-alone solution (i.e., the Ab Ovo Ground Services Industry Solution – “GSIS”) that has the possibility to integrate with other ground services at the same airport, to share operational information and create a joint schedule.
Our solution is adapted to your business for a 100% fit.
The GSIS necessitates that information is up-to-date and consistent, and the integration of the various ground services with Advanced Planning & Scheduling (i.e., “APS”) functionality in one central system ensures this consistency. The integration of scheduling knowledge is advantageous as this knowledge contains the schedule constraints, fit of jobs and resources, etc. The planner normally maintains this knowledge and uses it while creating the schedule.
Adding the knowledge of the planner into the solution reduces the human interaction within the planning process, and this will decrease the costs of and the number of errors during the planning process. Planning constraints will be checked by the system, while the planner can focus on taking the right decisions.

Ab Ovo Ground Services Industry Solution
As mentioned, the Ground Services Industry Solution ( GSIS ) is a stand-alone APS approach for ground service activities like catering, fueling, push-back, towing and baggage handling. The GSIS ensures better control over the planning and scheduling processes. An implementation will result in:
- Optimization of service delivery speed
- Maintenance of consistent delivery performance
- Increase in punctuality
- Increase in productivity
- Improved management of the human and physical resources
- Improved cost control
- Improved management of information related to Key Performance Indicators (i.e., “KPI’s”)
The GSIS is designed for easy integration with existing planning applications and flight information systems. Ab Ovo implemented this for KLM Catering Services.
Ab Ovo Collaborative Ground Services Industry Solution
The Collaborative Ground Services Industry Solution ( C-GSIS ) provides an overall vision for planning and scheduling of ground services. This integrated solution contains monitoring and controlling mechanisms and facilitates the interaction and optimization between various services to increase efficiency, including:
- Overall optimization of the delivery speed of ground services
- Overall view for the central ground service department
- Shared notifications of conflicts in planning
- Minimization of unavoidable disruptions to ground services
- Understanding of conflicts between the planning of the various services
- A central overview of delays
- Ability to reschedule due to delayed aircrafts
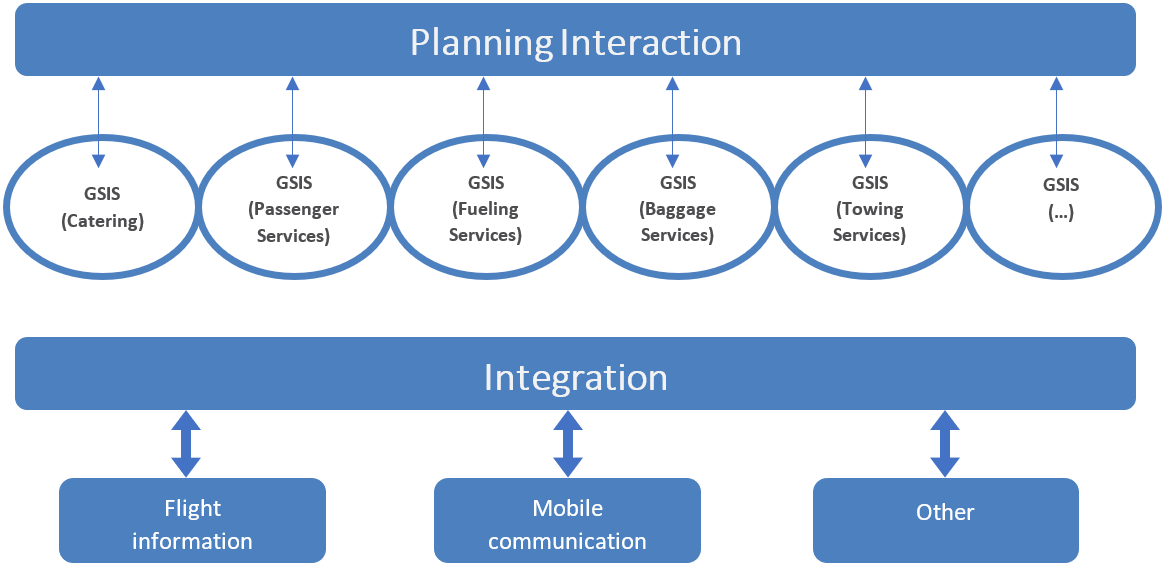
The overall coordination of the total range of services that are offered can be fully supported if all de-centralized GSIS’s are integrated under the C-GSIS); however, the collaborative solution can also be operational and useful when a limited number of services are supported.
The C-GSIS offers the possibility to distinguish conflicts between the planning of the various services because relevant knowledge is used to determine the planning of separate jobs.
The knowledge to prevent conflicts includes:
- Sequence of activities (e.g., push-back is the final service)
- Parallel planning of jobs (e.g., some aircraft types cannot be catered and fueled at the same time)
- Skills (e.g., resources need specific skills in order to execute certain job types)
- Duration of the various jobs and related jobs (driving time, positioning time, loading and unloading time)
The C-GSIS offers the possibility to dispatch an order to achieve a minimum number of delayed aircrafts. Choices can be made based on cost, goodwill, delivery performance, etc. These different choices can all be maintained within the system and will be valid for the specific carriers, flight numbers, aircraft types, ranges of destination, etc.
Business Benefits
The benefits of the C-GSIS are:
Phased development. The development of the application can be realized in phases; stepwise, desired functionality can be realized.
100% fit. The C-GSIS is characterized by a 100% fit to the customers planning model. This means that all desired functionality can be achieved.
Existing framework. The C-GSIS uses a framework that contains a range of standard modules, which support approximately 75% of necessary functionality. Therefore, the time needed to develop the 100% fit is limited.
Flight information system. The flight information system delivers information for the aircraft visits on which the planning is based; jobs are automatically generated from the flight information.
Data communication. One of the optional features is the wireless communication between the C-GSIS and a handheld computer used by personnel. The ground personnel obtain their orders and provide feedback as to the progress of their jobs by means of a handheld device.
Real-time monitoring. The overall monitoring function is used for monitoring the system and provides insight concerning bottlenecks in planning.
Fewer delays. By having an overall view and the ability to dispatch all offered services, the planner can decide to delay the servicing of one or more airplanes in favor of other airplanes based on departure time.
Planning horizon. The horizon of the planning is sometimes limited to a horizon of a few hours. The C-GSIS allows the better planning of resources (e.g., manpower, trucks, tractors, etc.) during this constrained time.
Measurement & Control. Measurement is key to process improvement. Real-time monitoring of activities is possible.
Feedback. The C-GSIS facilitates up-to-date planning of the departure of aircrafts. This understanding can be used as feedback for the flight information system.

Financial Benefits
- Reduce costs (penalties). More information concerning the planning process will improve the planning process, and these improvements can be measured in terms of KPI’s. This can include cost penalties due to delayed aircrafts – this can have impacts on efficiency and be compared to specific Service Level Agreements (i.e., “SLA’s”).
- Investment. Ab Ovo’s familiarity with APS for ground services enables a modular approach to reduce investment – this means that we have “off-the-shelf” solutions/functionality.
- Short development period. The modular approach minimizes time-to-market.
- ROI. The mentioned financial benefits result in a short ROI-period.
Functionality
The functionality of the C-GSIS is based on a number of basic functions:
Automatic job generation
This depends on carrier, aircraft type, flight number, origin and destination areas.
Resource allocation
Allocation of the resources is optimized and aligned with defined KPI’s.
Automation
This concerns the automatic updating of flight information.
Since this functionality is largely off-the-shelf, Ab Ovo can quickly implement it.
The inputs for the C-GSIS are obtained from one or more sources — these sources are usually flight information systems. An integrated model shares this information, and the various services (e.g., fueling, catering, push-back, etc.) can generate their jobs based on this information. These separate activities are united to form an overall ground services plan.
This overall planning is a mechanism to address (and solve) many of the bottlenecks in planning and can also be a mechanism to update the flight information system. In case of delays, the overall plan is able to decide which aircraft is best positioned to be delayed in order to allow re-planning of the resources at the different ground service providers. The result of this action influences the flight schedule.
Graphic User Interface
Ab Ovo works to build an intuitive GUI to promote acceptance of the C-GSIS. The following is provided for the user:
- Job overview.
The input is flight information, which is translated into jobs, which can be displayed to provide an overview of the desired information. - Job planning.
Planning requires simple interaction with the system; constraints can be added and maintained by the key user. - Resource allocation.
The planned orders should be carried out by resources (e.g., manpower, trucks, trailers, etc.) and these resources are linked to jobs. - Gantt chart.
The Gantt chart shows the sequence of jobs to be handled. The color of the objects shows types of jobs and whether constraints are violated or not. - Resource capacity charts.
Charts per resource type (trucks, drivers, loaders, etc) that show the workload over time in combination with the available resources. - Job dispatching.
The outcome of the planning is communicated to the drivers/employees. There are various methods for the interaction between planners and human resources. Ab Ovo uses modern technology to implement this interaction by enabling the use of handheld computers displaying the orders to be carried out. - Tuned scope.
The role and the department of the user determine the functionality and obtained information from the planning system. - Knowledge maintenance.
An optimized plan can be achieved when all restrictions, best-fit and optimal circumstances are known by the planning system. This can include driving times versus distances, maneuvering time at the aircraft and docking site, aircraft types, restrictions with the trucks/trailers, skills of drivers, etc.




